

Coli 0157 is a specific serotype of Escherichia that can cause haemolytic uraemic syndrome (HUS). Coli usually causes intra-abdominal and urinary infections.Į. LocationsĬommonly found in the lower intestines. Shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli (STEC) - Shigella-like dysenteryĮscherichia are rod-shaped (bacilli), facultative anaerobic microorganisms.Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) - Haemolytic uraemic syndrome.Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) - Gastroenteritis.Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) - Gastroenteritis.Different serotypes of Escherichia coli are shown below. Some strains, notably Escherichia coli, are pathogenic to humans causing numerous infections. Most members of Escherichia are common commensals in the gut microflora. mycoplasma).Įscherichia are commonly associated with urinary and gastrointestinal infections and are a major cause of nosocomial infections (hospital-acquired). NOTE: Some bacteria do not have a cell wall (e.g. When broken down and released into the circulation, lipid A stimulates a profound inflammatory response that can lead to septic shock. LPS is the key feature of gram negative organisms that contains lipid A. Beneath the outer membrane is a smaller peptidoglycan layer compared to gram positive organisms and then the cell membrane. Gram-negative organisms: have an outer cell membrane that contains lipopolysaccharides(LPS).Underneath the peptidoglycan layers is the cell membrane Gram-positive organisms: have a thick peptidoglycan layer composed of polysaccharides and charged amino acids interlaced with other major polymers like teichoic acid.
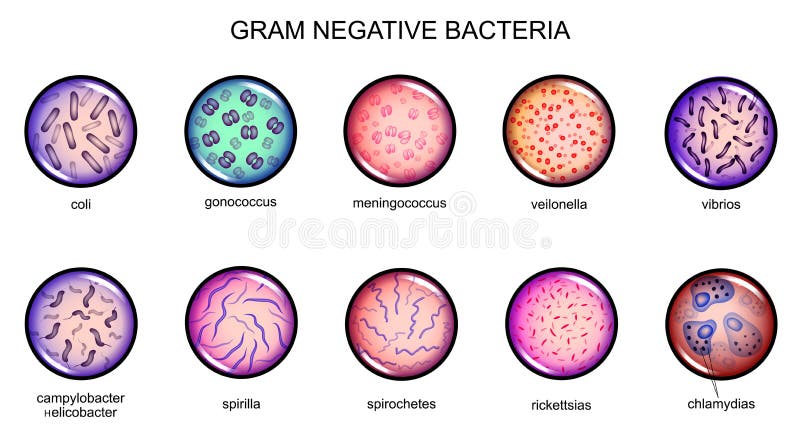
These are the two major groups of bacteria. The cell wall differs depending on whether the organisms is gram-positive or gram-negative. The cell wall forms the outer aspect of bacteria, which protects it against host immune defences and external osmotic pressures. The general structure of a bacterium includes the cell wall, cell membrane, capsule, flagella, fimbriae, nuclear material, cytoplasm and other intracellular components.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
